Source: Living Health
In the world of design and the arts, it is very important to consider psychology, since through it we can transmit emotions and persuade the public, in addition to understanding how they perceive the message that has been sent to them.
In this article, we are going to talk about Gestalt principles in graphic design, and how they are a useful tool to understand how visual perception works, and why some visual elements work in one way or another.
We will find out what are the different laws that surrounds the Gestalt, and we will put examples of them in the world of design and advertising.
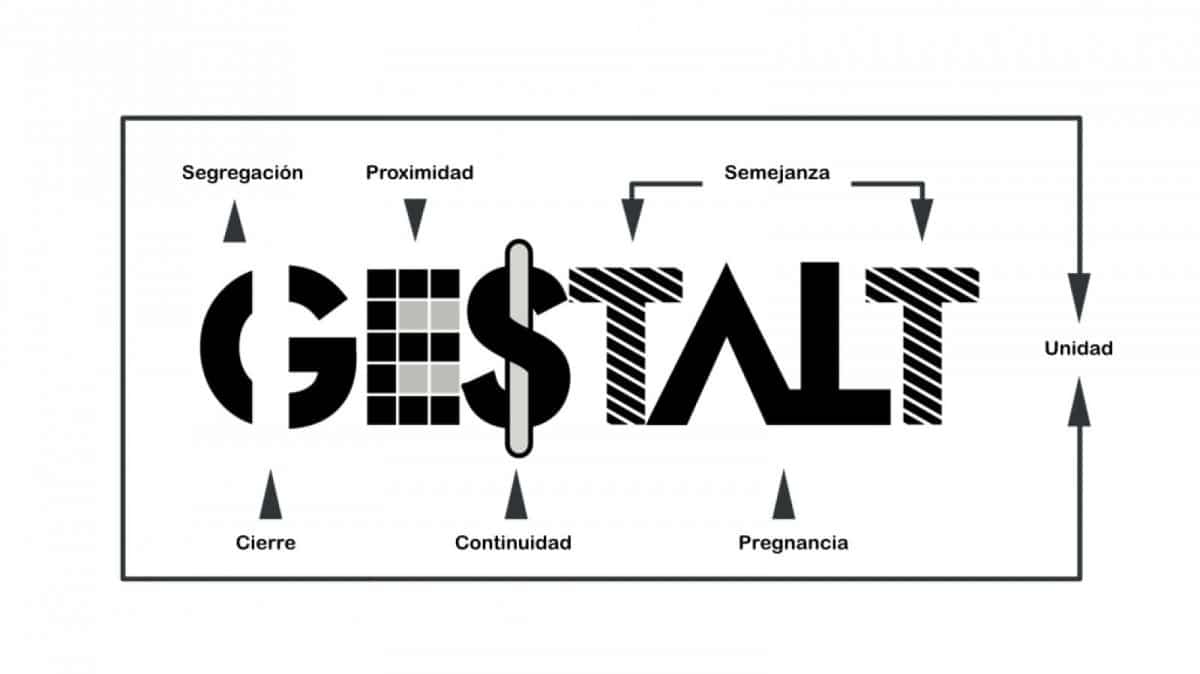
What is Gestalt?

The Gestalt theory or psychology of form, is a psychological trend that emerged in Germany around 1920, and that its principles are based on the theory of visual perception. The principles that Gestalt collects have evolved over time thanks to various researchers.
In the world of design, it is very common to take into account the six basic principles of visual perception that Gestalt presents us when designing, since with them we can create designs that engage viewers.
Gestalt Laws
We are going to focus on the six principles that are most used in the world of design and that we will recognize and understand very quickly.
similarity principle
The similarity principle will appear when objects seen appear similar to each other, this leads the viewer to perceive it as a balanced whole.
Objects share visual elements such as color, shape, size, etc. The greater this resemblance, the more coherent the whole is.

This principle is present in the old image of Mulberry, the luxury leather fashion house. The logo is inspired by the mulberry trees that the creator of the brand saw on his way to school. Focusing on that image is where we can see that this principle appears since they make use of basic shapes alluding to the top of the tree.
Continuity principle
In this principle, it is the eye that visually creates the continuity of a line, usually on curved lines, these elements are seen in a related way even though there is a break in that line.
In design, this principle can be used to direct our gaze through the use of a child element. Once we focus our sight, we move our eyes in the direction that marks us.

A clear example of this principle is the Coca Cola logo, in which we can see that its first C is the one that marks the route that our eyes have to take, the same happens with the second capital C.
closing principle
The closure principle occurs when an image is incomplete or poorly closed, and it is our brain that closes those spaces when you perceive them. Closed shapes are perceived as more stable shapes, and that's why our brain tends to complete an image.
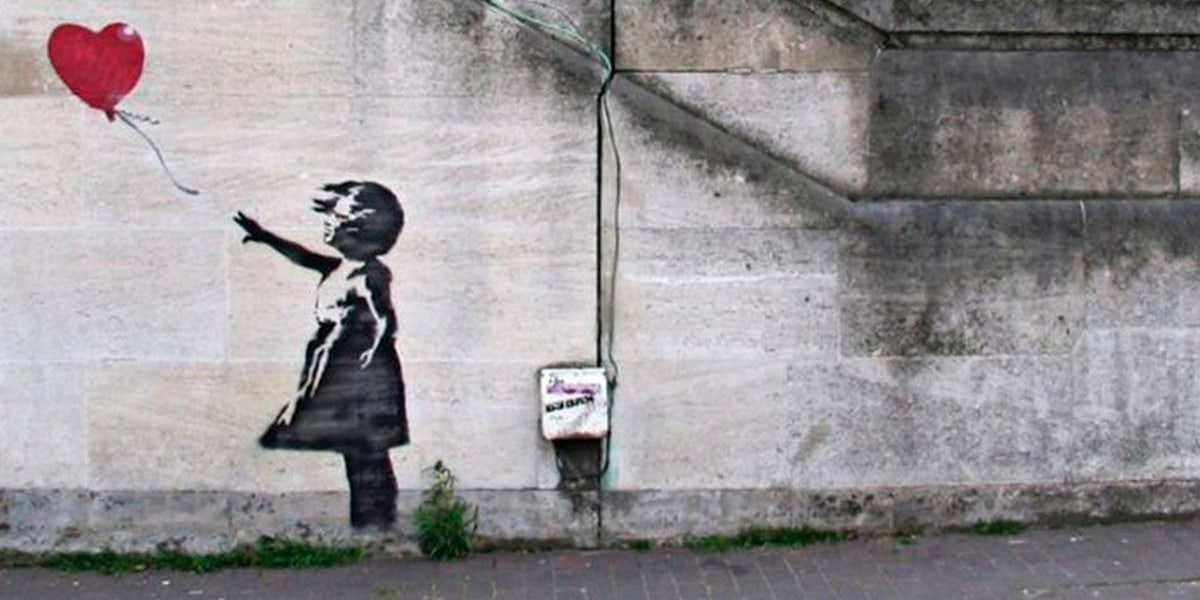

It is a widely used technique in the art world and one of its greatest pioneers is the world-renowned artist Banksy. In this work by Banksy, he uses the closure principle to create the figure of a girl and a balloon, although the shape of both elements is not completely closed, it is our brain that does it.

We can also see it in the Champions League logo, our mind is in charge of closing the image and creating the image of the ball.
proximity principle
This principle is based on the theory that elements that are located closer tend to be seen as a set and to separate, to isolate oneself from the rest. A group association is created between such similar objects.
For that group association to exist, the objects they have to share similar characteristics with each other, such as shape, size, color, texture, among other visual aspects.

One of the clearest examples where we can observe this principle is in the Unilever logo, in which we can see that the elements that make up its image share visual aspects such as size, color and thickness.
Principle of figure and ground
This principle embraces the idea that the eye tends to see an object by isolating its surroundings, separating the objects around it.
The figure would be the element that is in a space and stands out from the rest of the elements, on the other hand, the background is everything that is not a figure. It is our eyes that want to see the figure and leave the background in the background.
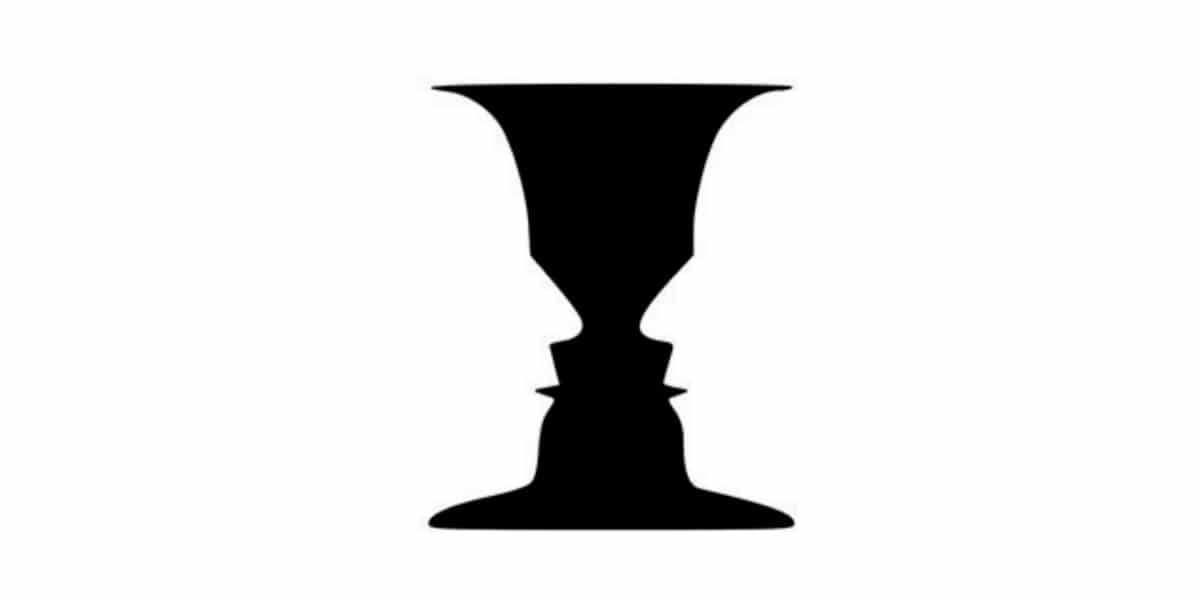

An example that we have all seen is the image in which we can see a candlestick made up of two faces in profile. In graphic design, we can usually find this principle in posters, such as the one below from Noma Bar together with the designer Tanya Holbrook, for IBM.

symmetry principle
This principle says that visual elements should be organized and symmetrical, they should not give a feeling of disorder or lack of balance, since the spectators will not understand the message that you want to convey.
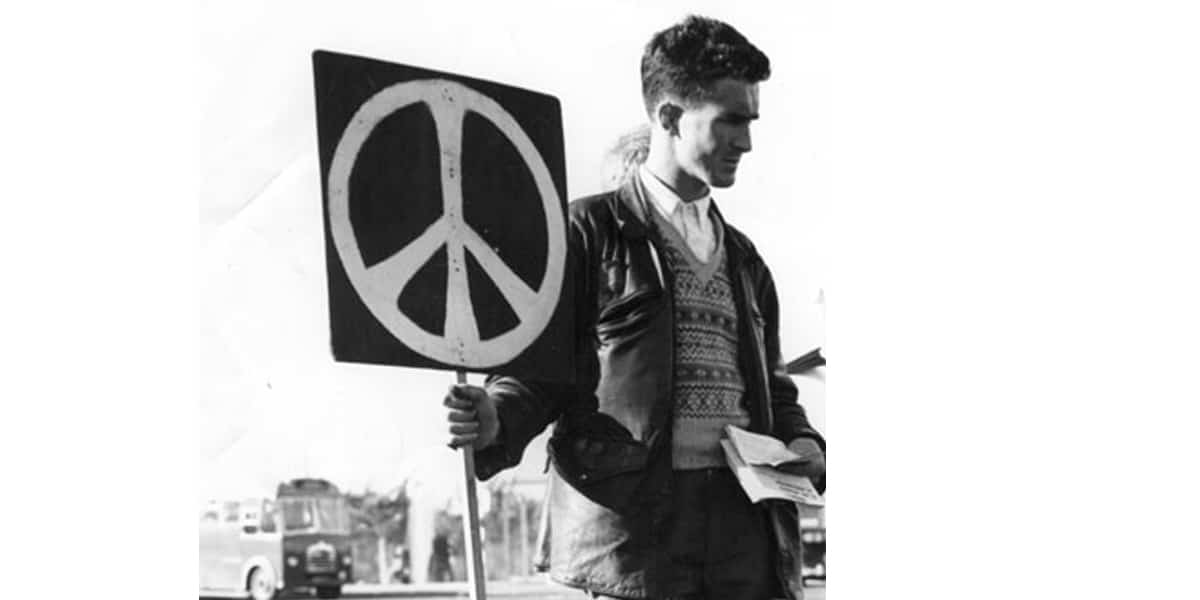

The peace symbol as we know it today, but was actually created as a symbol of nuclear disarmament, created by Gerald Holtom in 1958 is an example of the law of symmetry.
As you have seen, Gestalt principles are very present in the world of design and the arts. For a design to work properly it has to be perceived in its entirety, it has to be built based on the needs of the recipient.
Gestalt principles they are a fundamental tool, since they are helpful in focusing the viewer's attention and to organize the different visual elements in an effective way, which causes the viewer, when viewing that image, to stimulate a feeling, an emotion, even his own creativity.
As designers, the main idea that we have to keep in mind is that it is essential to understand how the spectators, our public, perceive the objects and that is why Gestalt is very useful to analyze how it works.