
Surely more than once, while browsing the Internet, you have come across some other image format that did not sound familiar to you. In fact, relatively recently you could see a change since in the image search engine (Google, for example), when saving an image, the typical jpg did not appear, but webp. And there are many image formats.
But What are image formats really? How many there are? And which are the most used? Today, we talk about them.
What are image formats?

Image formats, also known as image file formats, are actually a way of storing that image's data without having to compress it, although it can also be compressed (losing or not data) or transformed into vectors.
In short, we are talking about a digital file containing all the data necessary for the image to be formed. This data is pixels, since it is what makes up the image. Each of these pixels is made up of a number of bits that are used to determine the color of the photo. Hence, depending on the formats, an image may have better or worse quality.
Types of image formats

On the Internet you can find that the most common are usually jpg (or jpeg), png or gif. But actually there are many types of image formats. We talk about each one of them.
JPEG, JPG, JFIF

Of these acronyms, the one you will know least is undoubtedly the last one, since it is not common to see it on the Internet. However, all of them do reference to Join Photograghic Experts Group, or what is the same: JPEG.
What it does is compress an image losing data so that it weighs less. To do this, it uses the JFIF format, JPEG File Interchange Format.
This is the most common on the Internet and is characterized by the following:
- 8-bit grayscale
- 24-bit color images (uses 8 bits for each RGB color (green, red, and blue).
- Lossy compression (which helps make it smaller).
- Generational degradation. That is, when they are edited and saved many times they lose more quality.
There is a variant, which is called JPEG 2000. This may allow lossy or lossless compression but is not well known. In fact, it is only used in film editing and distribution, for example, for movie frames.
TIFF
This name refers to Tagged Image File Format. It is a flexible format that you can find on the Internet as TIFF or TIF, although it is not very common.
Among the features it has are:
- Be able to save compressed images with or without loss.
- Not being supported in many web browsers.
- Handles specific color spaces, like CMYK, OCR, etc.
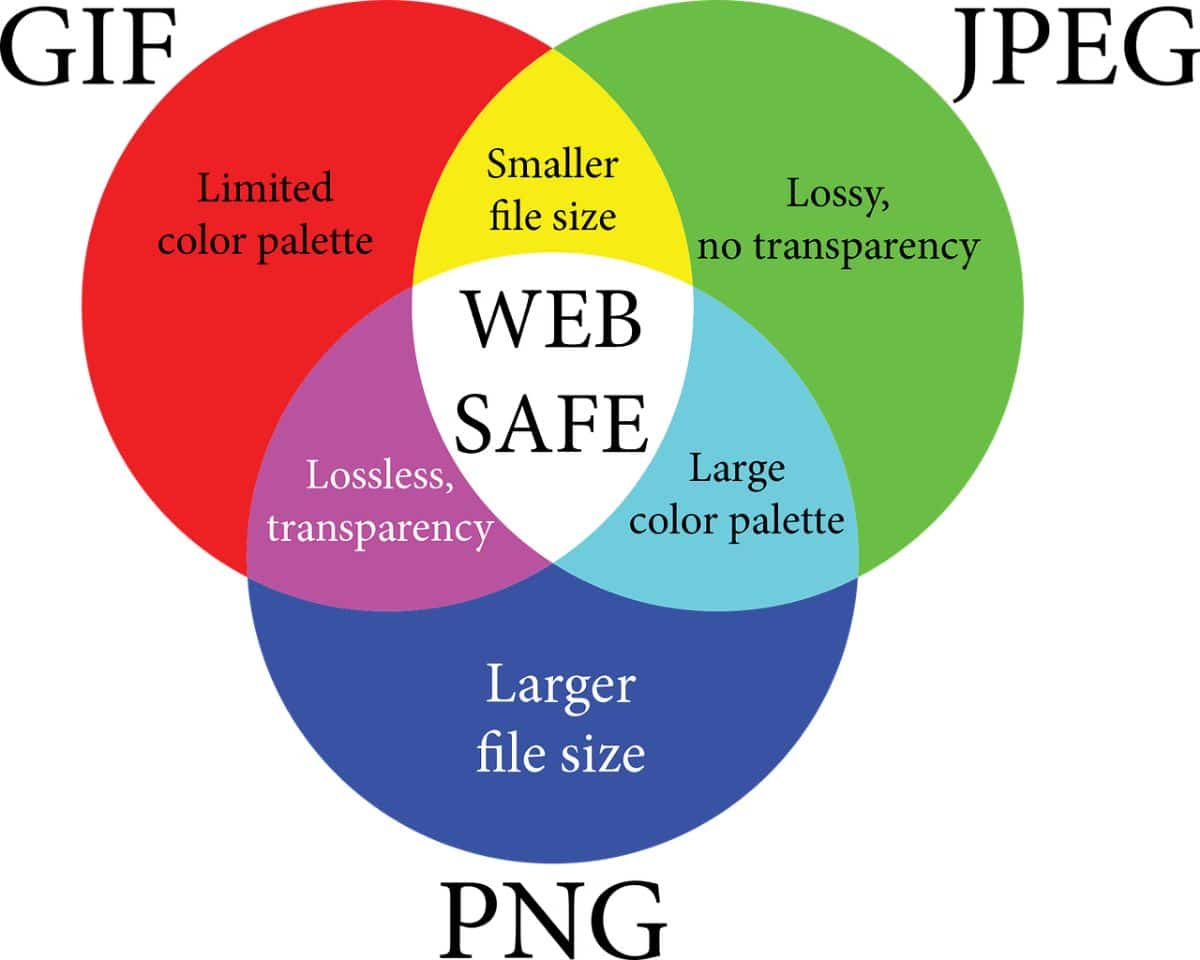
GIF

GIF, or Graphics Interchange Format, is one of the most commonly used image formats for creating mostly animationsas it allows you to record motion picture files. However, it is not exclusive for this, it is also used for photos because it compresses without loss, that is, it maintains the quality of the photograph that you save in this format.
It is characterized by saving all the information of the image in a table called the color palette, which can contain up to 256 colors (8 bits). They are easy to find on the Internet, although they are mainly used for logos (without a background to make it transparent), animations, clip arts, etc.
PNG

PNG stands for Portable Network Graphics. At first it was not widely used (we are talking about 1996) but now you can easily find images and photos with this format.
Among its features are:
- Compress images without loss.
- Offer a color depth of up to 24 bits (and not the 8 for example of the previous ones).
- It has a 32-bit alpha channel.
- It cannot generate animations.
- Accepts transparencies and semi-transparencies.
Today It is mostly used on images and graphics, logos, lossless photos, photos that require transparency, etc.
PSD

This type of file is the one that is created through Adobe Photoshop (or similar). It is used to save the image with the highest quality, without losing any of the work that you have been able to do. In fact, it has the advantage that it saves everything, including changes, layers, styles ... in such a way that you can retouch it later if you are not convinced by the result without having to start from scratch.
The problem is that you cannot see these types of images in the browser, they can only be opened with a specific program to make them work.
WebP
The WebP image format is one of the least known, but one that you can easily find on the Internet now. Is a format that saves the image with dissipated compression and without image loss.
The objective of this format is to have a smaller size so that, in return, it loads the page faster. Designed by Google, it is based on the VP8 intra-encoding framework and has a RIFF container.
SVG

SVG stands for Scalable Vector Graphics. It is one of the image formats that you find totally free and that focuses mainly on vectors. As with GIF, you can also animate some images with SVG. The only problem is that these types of formats are not yet supported by social networks.
Image Formats: EPS
EPS is Encapsulated PostScript. Actually, it is a format that created Adobe, but the PDF was replacing it.
Image formats: BMP

BMP stands for Bitmap. It is one of the formats that began to be used in the 90s and that were characterized by making compressions with very little loss of quality, which implied that the size of each file was quite large (in return the resolution of the image was perfect).
Today it is still used, although less than other image formats.
Other lesser known formats
Apart from those that we have mentioned, there are other image formats that are less popularly known, but professionally, they can be more used. These are:
- Exif. This is a file similar to JPEG and TIFF. What it does is record multiple data such as camera settings, when the photo was taken, degree of exposure, etc.
- PPM, PGM, PBM or PNM.
- HEIF.
- RAW.
- AI.